by Charles Oropallo | May 17, 2025 | Internet, Security
 Cybercriminals are getting smarter every day. They’re not just sending those obvious “Nigerian Prince” emails anymore. Today’s scammers use sophisticated tactics that can fool even tech-savvy people.
Cybercriminals are getting smarter every day. They’re not just sending those obvious “Nigerian Prince” emails anymore. Today’s scammers use sophisticated tactics that can fool even tech-savvy people.
Let’s break down the three main types of social engineering attacks you need to know about. We’ll cover phishing, smishing, and vishing – plus some sneaky new tricks that emerged in 2025.
What’s the Difference Between Phishing, Smishing, and Vishing?
Think of these three methods as different doors criminals use to break into your digital life. Each one targets a different communication channel you use every day.
Phishing happens through email and fake websites. Scammers impersonate trusted companies like your bank or Amazon. They’ll send urgent messages claiming your account needs immediate attention. The goal? Get you to click malicious links or download infected attachments.
Smishing uses text messages and messaging apps like WhatsApp. These texts often claim your package is delayed or your account is compromised. They include suspicious links that steal your information when clicked.
Vishing involves phone calls or voicemails. Scammers pretend to be from your bank, tech support, or government agencies. They use high-pressure tactics to make you reveal passwords or account numbers over the phone.
How Phishing Really Works (It’s More Clever Than You Think)
Modern phishing emails look incredibly convincing. Scammers copy official logos, use proper grammar, and mirror legitimate company websites perfectly.
Here’s a real example: You receive an email from “PayPal” saying someone tried to access your account. The email looks authentic, complete with PayPal’s logo and formatting. It includes a link to “verify your identity.”
But when you click that link, you land on a fake PayPal login page. The moment you enter your credentials, criminals capture them. Within minutes, they’re accessing your real PayPal account.
The scary part? These fake websites often use HTTPS encryption, so you’ll see that “secure” lock icon in your browser. Don’t let that fool you – criminals can get SSL certificates too.
Smishing: Why Text Message Scams Work So Well
People trust text messages more than emails. We’re conditioned to respond quickly to texts, especially ones that seem urgent.
Smishing attacks often use shortened URLs like bit.ly links. These hide the real destination, making it impossible to see where you’re actually going. The messages create artificial urgency: “Your package will be returned if you don’t respond in 24 hours!”
Here’s what makes smishing particularly dangerous: Most people don’t have security software on their phones like they do on computers. This makes mobile devices easier targets for malicious websites and downloads.
Think about how many important accounts are linked to your phone number. Your bank, email, social media – they all send verification codes via text. Criminals know this and exploit it ruthlessly.
Vishing: The Human Touch That Breaks Down Your Defenses
Voice phishing feels the most personal and urgent. There’s something about hearing another person’s voice that makes threats feel real and immediate.
Skilled vishers study their targets beforehand. They might know your name, where you bank, or recent purchases you’ve made. This inside knowledge makes their calls incredibly convincing.
Caller ID spoofing makes these calls appear to come from legitimate numbers. Your phone might display your bank’s actual customer service line, even though the call is coming from a criminal’s burner phone.
The pressure tactics are intense. They’ll claim your account has been compromised and you need to verify information “right now” to prevent further damage. They might transfer you between different “departments” to make the scam feel more authentic.
The New Tricks Criminals Started Using in 2025
Artificial Intelligence changed the game completely. AI-powered phishing creates personalized messages that perfectly mimic your colleagues’ or friends’ writing styles. These aren’t generic scam emails – they’re tailored specifically for you.
Clone Phishing takes emails you’ve actually received before and creates malicious copies. Remember that legitimate email from your bank last month? Criminals recreate it exactly, but replace the links with dangerous ones. Since you recognize the format, you’re more likely to trust it.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) targets companies by impersonating executives. An employee receives an email that appears to come from their CEO, requesting an urgent wire transfer or asking for sensitive customer data. These attacks often don’t include any attachments – they rely purely on social manipulation.
Deepfake voice technology now lets criminals clone someone’s voice from just a few minutes of audio. They might call pretending to be your boss, using AI-generated speech that sounds exactly like them.
Red Flags That Scream “This Is a Scam”
Your gut instinct is often right. If something feels off, it probably is. Here are specific warning signs to watch for:
Urgent language designed to bypass your critical thinking. Phrases like “immediate action required,” “account will be closed,” or “respond within 24 hours” are huge red flags.
Requests for sensitive information through email or text. Legitimate companies never ask for passwords, Social Security numbers, or account details this way. They already have this information.
Generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of using your actual name. Real companies typically address you personally in important communications.
Shortened URLs or suspicious links. Hover over any link before clicking to see where it actually goes. Be especially wary of URLs with random characters or unfamiliar domains.
Grammar and spelling mistakes in messages from “professional” organizations. While scammers have gotten better at this, many still make obvious errors.
Your Defense Strategy: Simple Steps That Actually Work
For email phishing: Never click links in suspicious emails. Instead, go directly to the company’s website by typing their URL into your browser. If the issue is real, you’ll see it when you log into your account normally.
For smishing: Don’t click text message links from unknown numbers. If the message claims to be from a company you do business with, use their official app or website instead.
For vishing: Hang up and call back using the official number from the company’s website. Real representatives won’t mind you verifying their identity this way.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all important accounts. Even if criminals steal your password, they won’t be able to access your accounts without the second verification step.
Keep your software updated. This includes your operating system, web browser, and antivirus programs. Updates often fix security vulnerabilities that criminals exploit.
When in Doubt, Verify Through a Different Channel
Here’s the golden rule: If someone contacts you claiming there’s a problem, verify it independently. Don’t use the contact information they provide – look it up yourself.
Call your bank using the number on your debit card. Log into your accounts directly rather than clicking email links. Check with IT before responding to urgent requests from “executives.”
This simple habit will protect you from 99% of social engineering attacks. Criminals count on you responding immediately without thinking it through.
Protecting Your Business and Family
Share this information with your employees and family members. Cybercriminals often target less tech-savvy individuals to get access to business networks or family finances.
Create a family or workplace policy: Never give out sensitive information over the phone or via email without verification. Make it clear that taking time to verify suspicious requests is always acceptable.
Consider using a password manager and teaching others to do the same. This makes it much harder for criminals to access multiple accounts even if they steal one password.
Remember, you don’t have to become a cybersecurity expert to stay safe. Following these basic guidelines and trusting your instincts will keep you ahead of most scammers.
If you’re concerned about your business’s email security or need help implementing better protection policies, our email security consulting services can help you create a comprehensive defense strategy.
The key is staying informed and remaining skeptical of unsolicited contacts asking for information or immediate action. When criminals can’t pressure you into quick decisions, their tactics usually fail.










by Charles Oropallo | Jun 30, 2022 | Do-It-Yourself, Email, Internet, Passwords, Security, Website Updates, WordPress
We at CharlesWorks are often asked by our web clients if their site is protected from malware and getting hacked. They also want to know if there site IS hacked, whether there be a charge to fix it.
The totally hack-proof website
The totally hack proof website has no access to it. So it’s not connected to the Internet. No one can view it. Such a website doesn’t sound like its of much use if no one can see it.
So, let’s agree that it is unrealistic to believe that a publicly accessible website can be totally hack-proof. Any website that is accessible via the public Internet is consistently subjected to attempts to break into it. Believe it or not, that’s the norm as opposed to the anomaly.
That being said, however, there ARE things you can do to mitigate website hacks. I have to stress the word mitigate here. Mitigation is defined as the action of reducing the severity, seriousness, or painfulness of something.
Site hacks are based on odds
My goal here is to simply remind you of what you most likely already know: that we can reduce the probability – the odds – of your site being hacked. We at CharlesWorks want that probability to be so low that it hopefully it doesn’t ever happen to you.
The major hacking causes
I have been operating CharlesWorks since 1998. In my experience, there appear to be two major reasons why sites get hacked:
-
- The access credentials/passwords have been compromised.
- The software that operates them wasn’t kept up to date.
Lets take a look at each of these below.
Compromised Access Credentials
Compromised passwords and bad actors gaining access to website login credentials is the major reason we see sites hacked. Think about this in terms of your car. You could have alarms on it. But if you make a copy of your car key and give it to someone, they can do whatever they like with the car. Whether its a drive along the beach or to rob a bank, your car is theirs to use with the key you gave them. Credentials – log in and passwords – work pretty much the same way.
CharlesWorks has many clients who want to be able to do things themselves. We are strong proponents of doing it yourself when it’s feasible and convenient. This is especially true for adding posts or page materials. It also makes sense when making other changes or modifications to your site. It is, after all, YOUR website.
However, many people fall prey to phishing schemes. Directly or indirectly, they usually end up tricked into giving out their website access credentials (as well as credentials to everything else they own). This is especially true if your email account is hacked and the hackers are able to access emails containing your website’s (and other) login credentials.
This problem is exacerbated if you have shared your website’s administrative or other access with others. Think of your emails containing various authorizations or login information as a potential weak link in a chain. If you have shared that information with others you have now created more weak links. This increases the odds of a potential compromise.
One of the best ways to mitigate these situations is to change your site’s access passwords so they are different than those possibly stored in your emails. And, to hope that anyone you may have shared your website access with has done the same.
Obviously, should site access be gained in such a manner, it would be your burden to have the site restored. I’ll expound upon this a little more at the end of this article.
Out of Date Security/Software Updates
Malware and virus protection on home computers operates a little differently than the same types of protection on servers. Website servers operate in the publicly accessible Internet. This results in many more entry points for potential issues. There are a number of very standard server protections available (which we utilize here at CharlesWorks).
After bad actors getting (or guessing) your passwords, the next major reason sites get hacked surrounds unapplied security updates and other software update issues. At CharlesWorks we mitigate such issues by running anti-malware software on our servers. Also, WordPress sites hosted on our servers are kept up to date automatically via automatic updating of the WordPress core as well as automatic updating of the the website’s plugins and themes.
There are literally thousands of individual pieces of software that must work in unison to operate most websites. These are developed by many more thousands of developers around the world. Unfortunately, no company can guarantee that a website will never get hacked. They can only mitigate security compromises and hope against the worst.
Restoring your Website
Regardless of which of the two situations above may have led to your website’s issues, your website will most likely need to be restored. That’s because after a bad actor or a hack back doors into the site will most likely have been installed for the bad actors to gain access again.
Many Internet companies claim to have automatic backups. In most of those, those backups are accessible to the user in their account. If the account is hacked, how safe do you suppose that is?
Some Internet companies delete and account upon a website being hacked. In those cases I have seen many left with no website or backup as a result.
What I believe is most important regarding this topic is the manner in which our WordPress sites are backed up every day for 30 days. Our backups are made to separate servers – external to those your the site operates on. For security reasons, the site administrators do not have access to these backups. So even with a site administrator’s compromised passwords there is no access to the backups. With these backups we can usually restore an average site in about 10-30 minutes if it needs restoring. And we can go back as far back as 30 days. We would only bill our web client for the 10-30 minutes (again – for an average website) which results in only a minor charge to restore it. Note that some websites are extremely large and require much more time to restore but these are very rare).
In my experience running CharlesWorks since 1998, we’ve built and handled more than 5,000 websites. At this point in time, I do not recall the last time a website we built and totally maintained was hacked (unfortunately I recall several instances of sites maintained by others that failed to ensure the site was updated and/or had their passwords compromised).
Sites getting hacked for out of date software happens far less frequently (if at all) when security updates are kept up to date and bad actors are kept out.
I hope this helps you understand a little more about this topic.










by Charles Oropallo | Dec 15, 2020 | Do-It-Yourself, Internet, Security, Technical Help, The CW Corner, Website Development, WordPress
Akismet provides a convenient and free way to protect your personal WordPress site or blog from spam.
Many times we’d like to allow comments to be left on our WordPress site. The hassle with this can be the tremendous amounts of spam that come through the forms on websites.
Akismet is a compact WordPress plugin that filters the incoming comments. It is pretty straightforward to use and pretty easy to set up as well.
Install the Akismet plugin
The first step in this process is to ensure that the Akismet plugin is installed in your WordPress website:
-
-
- Log into your WordPress website’s dashboard as an administrator
- Click on Plugins in the left dashboard navigation column
- Look and see if Akismet is listed – if it is – and it is not activated you can proceed to the Akismet Setup step below – otherwise
- Click on Add New under Plugins in the dashboard navigation column
- If you don’t see Akismet in the plugins, then in the text box to the right of the work Keyword in the row starting with Featured type in Akismet – then click on its Install Now button. Do not activate it yet.
Perform the Akismet Setup
To set up Akismet in your website, you will need an API code from the Akismet site. The first step in that process is to navigate to:
https://akismet.com/plans
This (as of the time of this writing) brings you to a page that should look similar to the screenshot below.
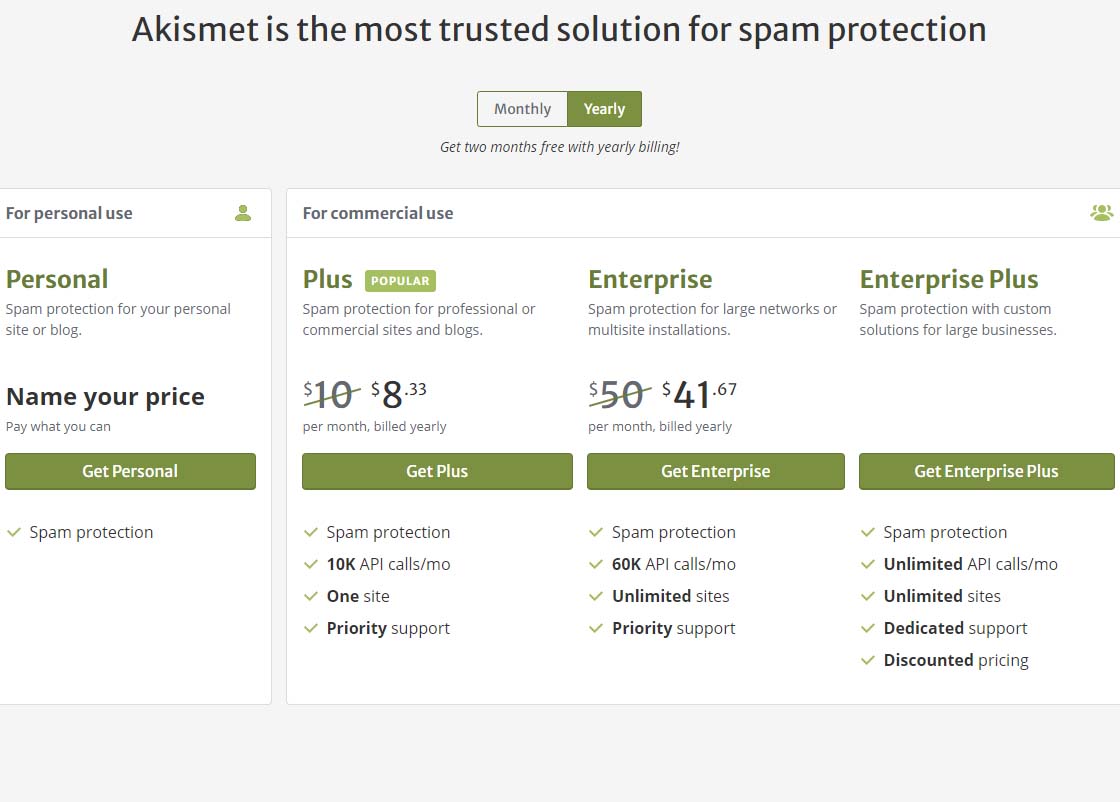 Akismet offering pricing page
Akismet offering pricing pageTo get the free version of Akismet comment spam protection, you will need to click on the Get Personal button on the above page.
Once you’ve done that, you should see a page similar to the one below. Before attempting to fill out anything on this page, we need to set that $36 / YEAR to $0 / YEAR. Click on the $36 / YEAR box and drag it to the left.
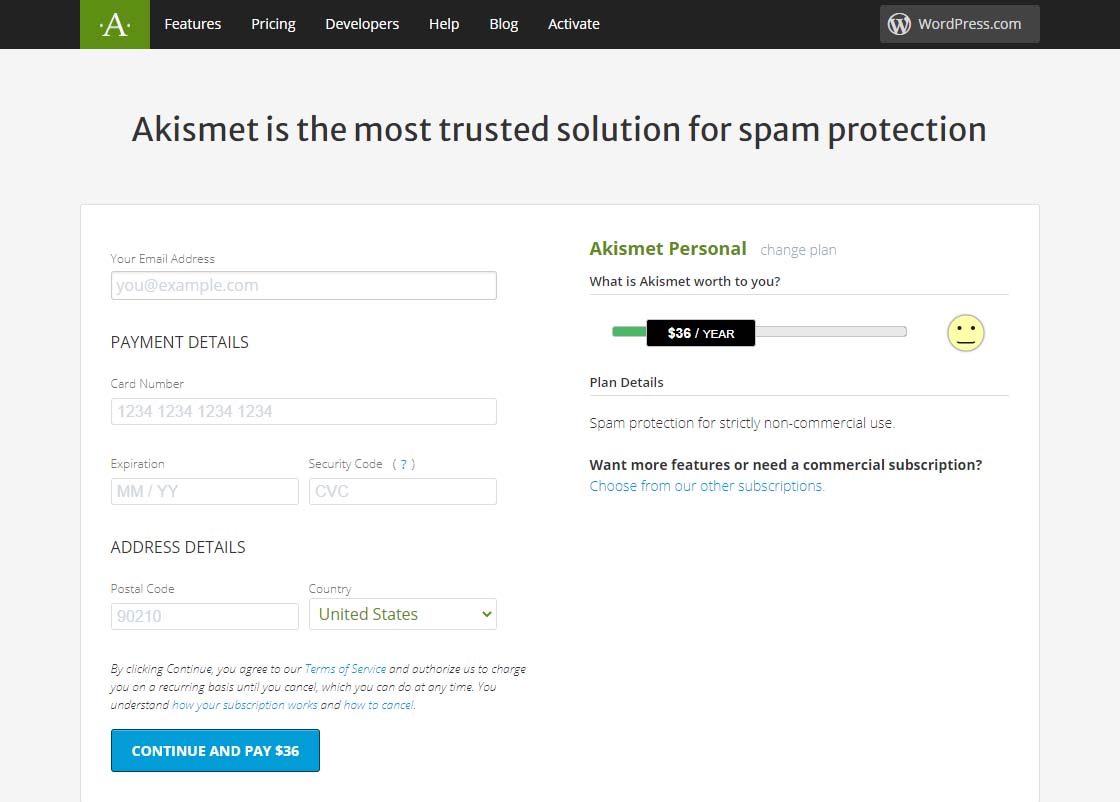 Akismet Default $36 per year page
Akismet Default $36 per year pageDragging that $36 / YEAR box to the left should change the page to display something like the one below showing 0$ / YEAR. You can also see that the information to fill in has changed.
Akismet $0 per year page
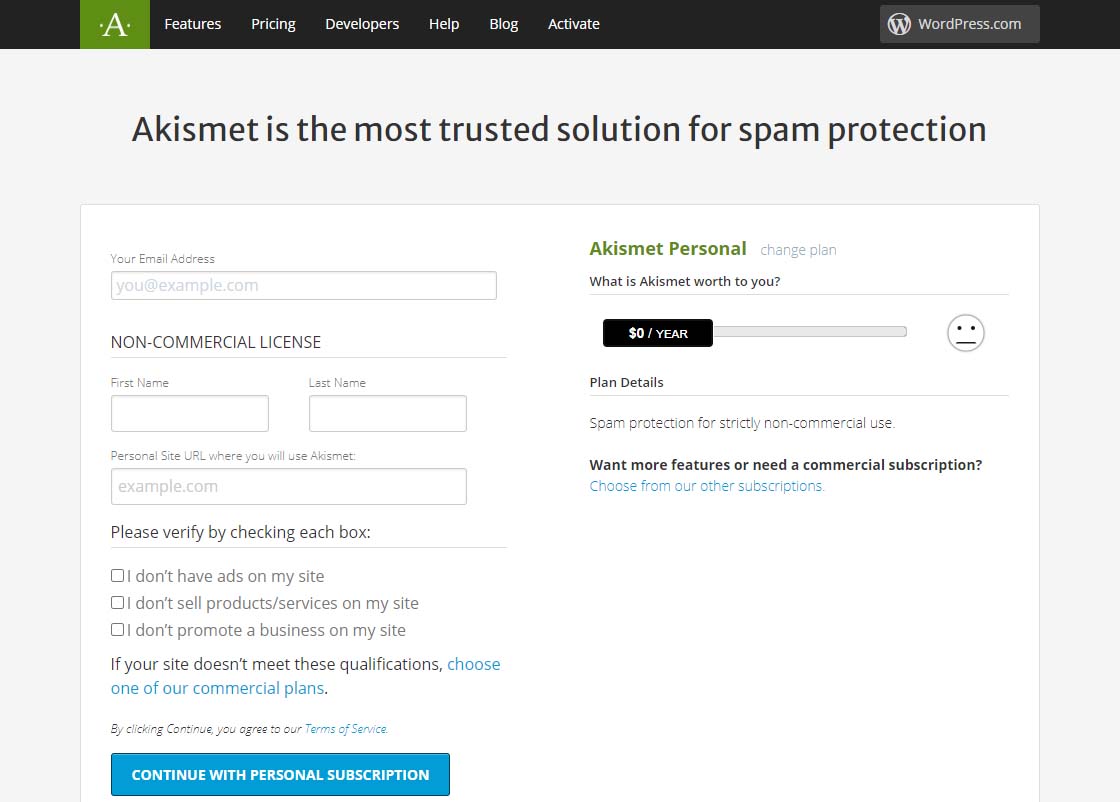 Akismet $0 per year page
Akismet $0 per year pageNow fill in the information completely. Note that you need to be able to check all three checkboxes indicating the following:
-
-
- you don’t have ads on your site
- you don’t sell products/services on your site
- you don’t promote a business on your site
If these are the case, then you will qualify for a free, personal plan.
All you have to do once you have gotten this far is follow the directions on the page below.
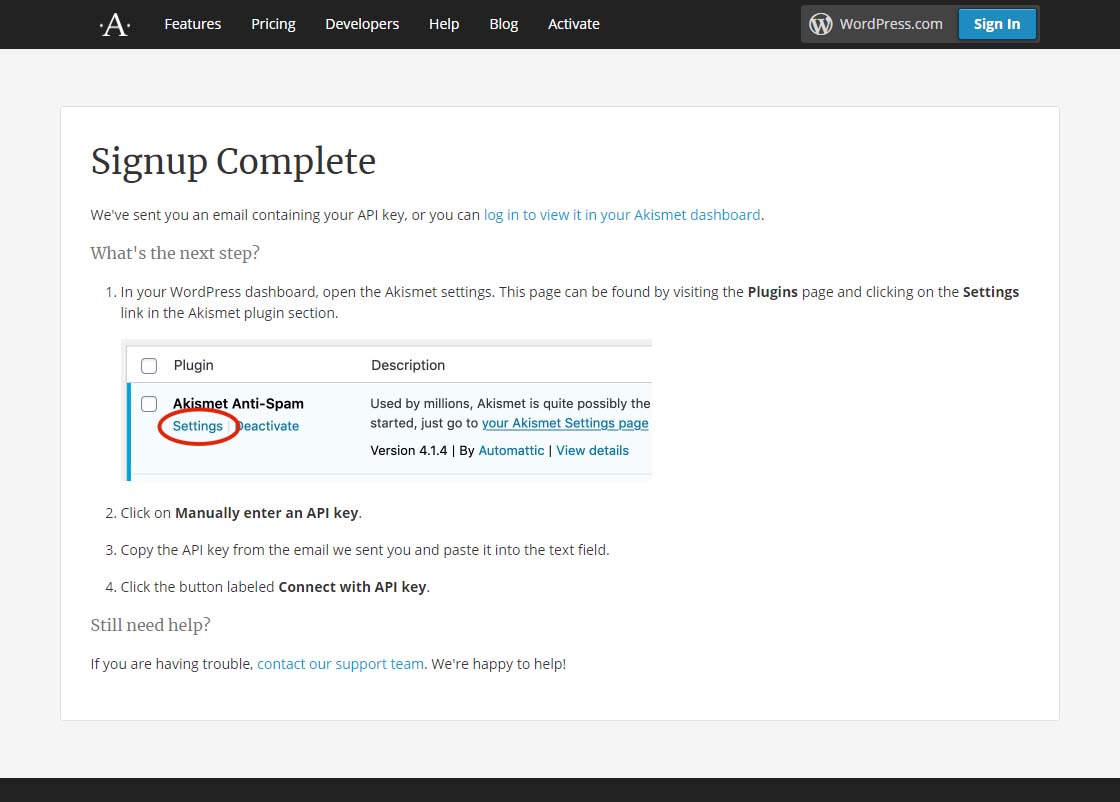 Akismet signup complete page
Akismet signup complete pageFinally, it is suggested that while on that settings page in Akismet, you can choose to show the number of approved comments beside each comment author and choose whether to show a privacy notice or not. Then just click the Save Changes button and you are on your way!










by Charles Oropallo | Oct 16, 2020 | Internet, SEO
Almost all businesses get the usual spam SEO (Search Engine Optimization) phone calls.
Recently, one of my web clients took one. As a result of such calls, she emailed me. She expressed a lot of concern about having been told very negative things about her web traffic and website operation. It sounded like he was trying to get her to spend money. Money she’d never see a return on her investment for.
High-pressure sales tactics are something I have instructed staff in all our years in business to avoid. CharlesWorks policy forbids selling clients anything they don’t need. The difficulty is that there are so many spammers and scammers out there sending the same messages that people believe them. You can tell the same lie a thousand times and it’s still a lie.
Among the thousands of websites we’ve handled, her particular business is very unique – especially during the COVID-19 epidemic. Her classes are limited regarding how many people she can have in them at any given time. I told her that she is the one who knows best what should be on her website. And she is the one who knows best what she has to offer and when she can offer it.
The nature of her business, it seemed to me, is based more on a following she has developed over time. And she is limited as to how many people at a time she can physically handle. And – much as I hate to say this – COVID is going to remain a thought in many people’s minds – at least through this upcoming winter season. Things will change when a vaccine is widely available. However, common sense dictates it will be a while before everyone generally has access to it.
I suggested she shouldn’t spend more than she absolutely has to – to just keep her business operational. Those small business owners who can stay in business through this pandemic will be the ones who do great once they reach the other side of this.
It’s troubling that someone had pressured her enough to do work on her site that she became stressed over it. Sales people who proceed with such a hard sell attitude are clearly desperate for work. Desperate people are not working with their customer’s best interest in mind. My advise is to not talk to these people.
My suggestions for dealing with these really hard line sales calls are:
- “Remove me from your calling list.” Tell them to remove you from their calling list. Once you say those words, they are supposed to do so by law. I regularly tell spammers this, and they generally don’t bother to call back.
- Block their phone number. Block their number through whatever mechanism your telephone carrier has set up to do that. I do this on a pretty regular basis with the robocalls (which are actually illegal in most cases) and take a few minutes to report them at the https://www.donotcall.gov/report.html site.
- Visit the National Do Not Call Registry. Go to https://www.donotcall.gov where you can put your phone numbers on the National Do Not Call Registry. Mine have been on this for many years.
While these suggestions don’t stop all the spam calls you’ll get, they do stop many.
Every small business owner can and should review their website. They should ensure that everything is up to date for offerings and schedules. That only costs them a few minutes. Because CharlesWorks charges for changes by the minute, those kinds of changes only incur those minutes of charges.
I hope this is helpful to you!










by Charles Oropallo | Sep 2, 2020 | Domains, Internet, SEO, The CW Corner
We’ve published plenty of information in the past about domain names. We’re always learning a little more and how to explain information to out clients as time passes.
Whether your domain name is for personal use or for your business, we hope you find the following tips to be helpful.
Keywords
Having words pertinent to your business in your domain are increasingly important. Simplistically put, search engine algorithms (the math formulae used to compute the importance or value of words contained in your site) rank the importance of web sites according to words. Many businesses use a domain name to describe the name of their business and, in addition to that, own domains which contain keywords which are present in their website.
Association
If possible, you should use the name of your business as all or part of one of your domain names. This will make it easier for your clients or potential clients to remember you and to find you on the web (like CharlesWorks.com – CharlesWorks is the name of our business).
General Names
More general domain names are most likely already registered to other businesses (of course it doesn’t hurt to check with us first). It’s still a good idea to have more general name(s) associated with your business as one of your domains (that’s why we also own HostingNH.net, which will take visitors to our CharlesWorks.net site).
TLDs
TLDs stands for Top Level Domains. TLDs are the extensions on the tail end of the domain, such as .biz, .club, .co, .com, .net, .org, .ws, etc. The most popular TLDs are .com and .net. If you find that your domain is already registered, you might try for an alternate TLD (for example, RobinSnow.com was already taken, so Robin acquired and uses RobinSnow.net).
Hyphenated Names
Although you can obtain them, we recommend not using hyphens for your business domain name. Most people who are searching for your site will not use a hyphen. You are better off to try a different TLD or a variation of your domain name.
Variations
Variations can be an option if your general business name is already registered (for example ScrapbookCabin.com was not available to one of our clients, so at the time she registered NHScrapbookCabin.com instead).
Relinquishing or giving up existing names
We have seen many horror stories concerning giving up existing domain names. Sometimes one will end up having to get a similar domain name because control over the preferred name could not be gained. An example would be where another party has control over one’s .com name and the website is down and the webmaster cannot be reached or is non-responsive. If we are to take over the services we would recommend getting the .net to the original .com of the domain name if it were available. This allows us to get the site up and at least people can be sent to that site pending transfer of the .com when it is possible. In some cases it never became possible and the site will continue using the .net domain.
Once a domain name has been in service, traffic is generated to it. For that reason, many expired or relinquished domain names are snatched up. One situation like this in the Manchester NH area involved a church giving up a domain name they did not want to use anymore (it was a version of the Church’s name that had been in use for many years and they just decided to change it and dropped the domain name). It saved them about $15 a year. However, the embarrassment was priceless when a porn company acquired that domain name and put a porn site up on it. The annual cost of a domain is truly cheap insurance against one’s domain name being used for phishing, porn, Viagra, or whatever.
There is absolutely no obligation of any kind to click the red button below and check out your domain possibilities!

Already have a domain name? Click on the red button below to transfer it so we can get you online here at CharlesWorks!

Or CALL CharlesWorks at 603-924-9867 9 am – 5 pm Monday through Friday or go to https://CharlesWorks.com/contact outside of regular hours and we will help you find one!










by Charles Oropallo | Aug 5, 2020 | Do-It-Yourself, Internet, Monadnock Shopper News, Shopper News, Website Development, Website Updates, WordPress
Something many folks overlook is occasionally checking their website’s functionality. I recommend doing this every couple weeks, but at minimum once a month.
Most websites and the servers they are on are subjected to ongoing software updates. Unless you are paying an additional fee for maintenance checks, it’s normal for things to occasionally break due to updates.
Most website owners are not paying additional fees for such maintenance. This means you really need to take the time to check:
– that the site appears to work properly
– that your hours of operation are correct
– that any website forms are working
– that email addresses are correct
The site operation and forms are most susceptible to software updates. If you have a good web developer, the fixes will happen quickly and it will not cost you too much.
Website maintenance should be thought of like automotive maintenance. We get oil changes. We get inspections. We even make modifications and do repairs to keep our vehicle operating the way we want. And our older vehicles can cost more to upkeep – just like older websites. As websites age, more work needs to be done to keep them secure and working as originally intended.
So check your site every now and then to keep things working and have the correct information out there!










 Cybercriminals are getting smarter every day. They’re not just sending those obvious “Nigerian Prince” emails anymore. Today’s scammers use sophisticated tactics that can fool even tech-savvy people.
Cybercriminals are getting smarter every day. They’re not just sending those obvious “Nigerian Prince” emails anymore. Today’s scammers use sophisticated tactics that can fool even tech-savvy people.








 European Union General Data Protection Regulation Compliant
European Union General Data Protection Regulation Compliant